Hot: Exhibition of IPR protection | Belt and Road | trade | 5G | Expo Beijing 2019
Editor: Chen Yue 丨Xinhua
06-14-2016 12:18 BJT
(4) Senior citizens' rights
The social security system for the aged is gradually being improved. The advanced-age allowance system was set up in 23 provinces (autonomous regions or municipalities directly under the central government). The old-age service allowance system for seniors in financial difficulty was carried out in 20 provinces (autonomous regions or municipalities directly under the central government). The nursing care allowance system for senior citizens with disabilities was launched in 8 provinces (autonomous regions or municipalities directly under the central government), while accident injury insurance for the elderly was introduced in 20 provinces (autonomous regions or municipalities directly under the central government).
Figure 2: Basics of national old-age services by the end of 2015
[GRAPHICS]CHINA-2012-2015-NATIONAL HUMAN RIGHTS ACTION PLAN(CN)
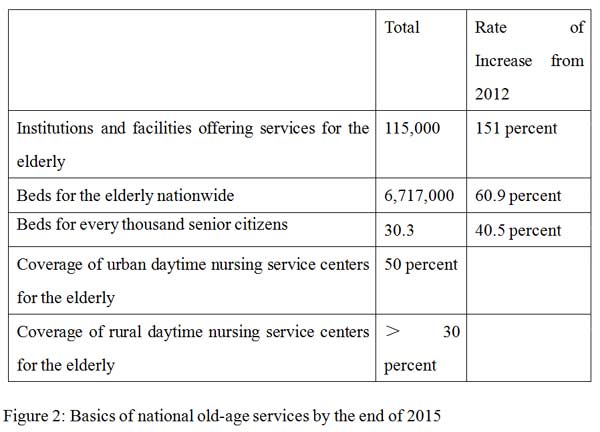
BEIJING, June 14, 2016 (Xinhua) -- Graphics shows basics of national old-age services by the end of 2015 in the Assessment Report on the Implementation of the National Human Rights Action Plan of China (2012-2015). (Xinhua)
The old-age social service system is being rapidly developed. By the end of 2015, there were 115,000 institutions and facilities offering services for the elderly, an increase of 151 percent from 2012. Home-based care service facilities for the aged covered basically all urban communities and over 50 percent of rural communities. By the end of 2015, there were a total of 6.717 million beds for the elderly nationwide, averaging 30.3 beds for every thousand senior citizens, 60.9 percent and 40.5 percent higher than those in 2012 respectively, which far exceeded the planned targets.
Senior citizens' cultural lives are being much enriched. By the end of 2015, there were 763,00 schools for the elderly across the country, 180 national-level and over 500 provincial-level community education pilot zones and demonstration zones, with the elderly accounting for over 60 percent of all participants in community education. There were 24 newspapers and 24 periodicals specially for the aged. The state provided a variety of digital cultural resources suitable for the elderly through various channels including the National Cultural Information Resources Sharing Project, the National Digital Culture Network and Chinese Culture Network TV.
(5) Rights of people with disabilities
The system on the protection of rights and interests of people with disabilities has been constantly improved. Since August 2012, the State Council successively formulated the Regulations on the Construction of a Barrier-free Environment and the Opinions on Accelerating the Development of a Well-off Course for People with Disabilities. The Supreme People's Procuratorate and the China Federation of the Disabled jointly distributed the Opinions on Effectively Protecting the Disabled Persons' Lawful Rights and Interests in Procuratorial Work. The state has established and improved mechanisms for the provision of legal assistance to the disabled, offering free, timely and convenient legal services for them.
People with disabilities are covered by social security. By 2015, the state had established a living subsidy system for the financially-challenged disabled population and nursing care allowances for the severely disabled across the country. There were 10.884 million people with disabilities in both urban and rural areas receiving minimum subsistence allowances, nearly 22.3 million people with disabilities in both urban and rural areas participating in social endowment insurance schemes and 3.023 million urban disabled dwellers participating in basic medical insurance schemes. During the period of 2012-2015, 4.962 million impoverished people with disabilities in rural areas were lifted out of poverty and 3.17 million poor disabled residents in rural areas received skills training, with the planned targets achieved in advance. The central government allocated a total of 3.74 billion yuan in rehabilitation and poverty-relief interest-deducted loans to support 743,000 impoverished disabled people. The state subsidized the renovation of dilapidated houses of 1.164 million rural households with disabled members.
The rehabilitation service for people with disabilities is being continuously enhanced. By the end of 2015, a total of 222,000 communities had established rehabilitation stations across the country. From 2012 to 2015, 8.544 million people with disabilities received community rehabilitation services. 12.466 million received basic rehabilitation services, achieving the expected goal ahead of schedule. From 2011 to 2015, the central government appropriated 432 million yuan to support rehabilitation training for 36,000 autistic children living in poverty. The supporting devices network covering both urban and rural areas is gradually being improved, offering 6.655 million supporting devices of various types.
The rights of people with disabilities to education, employment and culture are further guaranteed. The state implemented the Special Education Promotion Program (2014-2016), in an effort to fully expand the reach of special education and guarantee the ability and the quality of education and teaching. In 2015, there were 2,053 special education schools nationwide, with a total enrolment of 442,200 students and 50,300 full-time teachers. From 2012 to 2015, the central government appropriated 925 million yuan as a special education subsidy. The state carried out "the Special Education School Construction (Second Phase) Project" and allocated more than 2.442 billion yuan to support the infrastructure construction of 61 secondary vocational schools and vocational higher education institutions for people with disabilities and special normal schools for higher learning. In 2015, related departments published the Administrative Provisions on Disabled Persons' Participation in the National College Entrance Examination (temporary), in an effort to guarantee disabled people's right to receive education equally, and actively enhanced the revision work on the Education Regulations for the Disabled in order to strengthen legal guarantee. In 2012 they published the Notice on Strengthening Vocational Training for People with Disabilities to Promote Employment, so as to make sure that the disabled who wish to find a job can get relevant vocational training. Starting from 2014, the recruitment of disabled college graduates by Party and government organs, public institutions, state-owned enterprises and other units were guaranteed by policies. By the end of 2015, the state had set up reading rooms for people with visual impairments in public libraries at all levels, with an additional collection of 486,000 books in braille and 21,000 seats in those rooms. The state hugely expanded the scale of publications in braille. From 2011 to 2015, the state published 476 textbook titles with 692,000 copies in braille printed, 5,526 books for blind people with 1.3319 million copies printed, 1,138 big-word books for people with poor eyesight with 1.1234 million copies printed, and 2,400 types of audio books for the blind with a total length of 16,000 hours. The expected goals were achieved ahead of schedule and exceeded. Some excellent publication projects for the blind people were included in the National Publication Plan. Any qualified project was supported by the National Publication Fund.
The state quickened the construction and renovation of barrier-free facilities. Related departments revised and carried out the Management Measures for Air Transport of Persons with Disabilities and the Standards for Barrier-free Designs; published the Guiding Opinions on Strengthening the Construction of a Barrier-free Environment in Villages and Towns; and drew up and implemented the Requirements on Barrier-free Technologies for Website Design. It provided special seats for people with disabilities in all trains and allowed guide dogs to board trains. The state established additional barrier-free parking places on urban roads and in public parking areas within buildings and set up audio signal devices for people with visual impairments on pavement traffic signal facilities. It subsidized 573,000 families of the disabled to carry out renovation of barrier-free facilities.