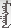By Belunn Se, senior industry observer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong province, China
July 13, China Telecom, along with Tianyi IoT Industry Alliance and Huawei, had jointly organized an official launch on the commercial use of a new generation of Internet of things — NB-IoT in Beijing.

(China Telecom launches commercial NB-IoT network in Beijing Photo from Internet)
China Telecom has focused on the three markets: Smart City, vertical industry and personal consumer, to deep plow around public utilities, intelligent transportation, energy production, intelligent logistics and security monitoring.
2017 appears to be the IoT business development breakthrough year for China Telecom, which owns the 800MHz band with advantages in faster speed, lower cost and better coverage:
In March, NB-IoT Smart Water project in Shenzhen launched;
In April, NB-IoT network for smart city construction opened in Yingtan, Jiangxi province;
In May, 310,000 NB-IoT commercial network stations completed;
In June, IoT open platform in Shanghai released;
And at the commercial launch, China Telecom announced an IoT service package: yearly package price at 20 Yuan/household/year, but also providing seven different stalls ranging from 2-8 years with discounts at different levels.
Beijing Telecom and other module manufacturers also signed a strategic cooperation agreement to build the Beijing IoT industry ecosystem; China Telecom, ofo (one of the prominent companies running shared bikes in China) and Huawei introduced NB-IoT technology based ofo smart bicycles;
China Telecom also promised to provide 300 million Yuan subsidy to support other IoT projects.

(Ofo joins hands with China Telecom, Huawei to boost bike-sharing in NB-IoT era with smart locks Photo from Internet)
NB-IoT offers lower power consumption, wider coverage and larger connections, as well as reducing response delays. Compared with the previous 2G lock, the NB-IoT smart lock can reduce the time delay from 25 seconds to 5 seconds.
Additionally, batteries in a sharing bicycle only lasts for 3 months, while the new yellow bicycle can continue on for more than 2 years.
Upgraded performance allows the bike to link up in remote areas where the previous signal was not covered. Due to limited capacity of 2G network crowded areas such as subways, the failure rate of unlocking reaches 30% at peak hours currently.
MIIT accelerates deployment to build 1.5 million NB-IoT base stations by 2020
On June 16, 2017, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) issued new measures.

(Typical application of Smart Manhole Cover Photo from Internet)
The measures settled targets on NB-IoT's entire industry chain of standards, devices, chips, modules, testing, applications and network development from 2017 to 2020.
The MIIT set a mission: By the end of 2017, NB-IoT base stations to reach 400,000 to cover major cities and provincial capital cities; by 2020, the scale of China's NB-IoT base stations to reach 1.5 million. .
Getting connected through Cloud, Channel and Devices
Infografic: IOT Architecture- Cloud, Channel, Device connecting scenarios
We have been using IoT already; especially while you read the article on a computer or mobile phone.
The "Internet of Things," has extended from the existing Internet that connects to computers via wired cables and has expanded to smartphones through 3G, 4G wireless communication.
The scale of future IoT is much larger than connecting computers and mobile phones, with estimates up to 50 billion sets of devices/things that would be connected to the internet by 2020.
Why NB-IoT?
Besides traditional Wired Cable connections, there are a wide-range of wireless communication choices that require specific applications, such as:
Coverage Distance (WAN/LAN)
Power Consumption (LPWAN)
Transmission Speed (Low/Medium/High)
Signal Penetration Capability
Maximum Devices Connection Capacity
Setting up and operations cost, etc.

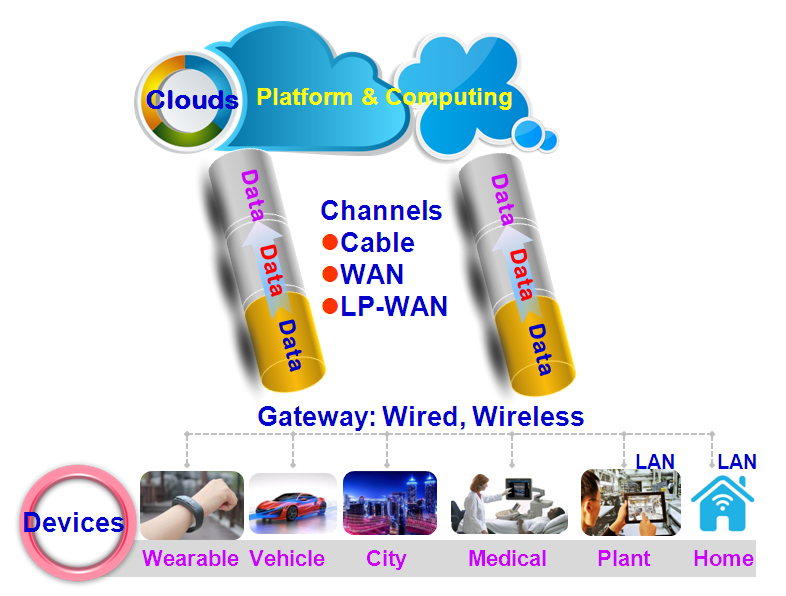
Infografic: Wireless Connection Choices
More and more "Things", around 60% of devices, especially meters and sensors, could get connected to the Internet mainly by LP-WAN (Low Power Wide-Area-Network).
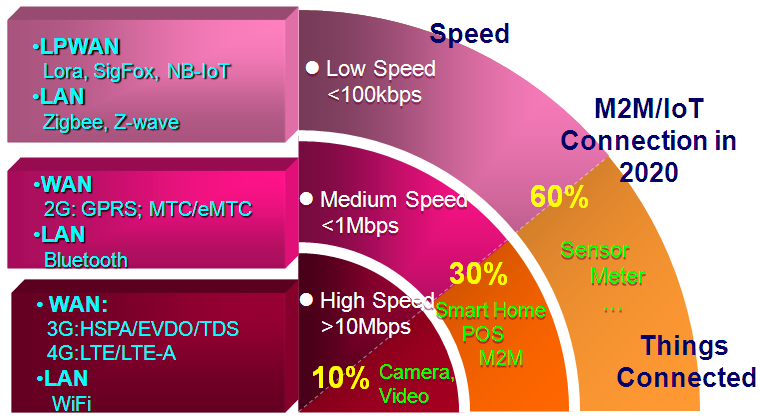
Infografic: Wireless Connection meeting different demands
NB-IoT can especially be exploited for it meets the requirements of those scenarios where relatively low power consumption and low speed of connection are demanded, but excellent penetration capacity is needed, for example, in bike-sharing lock applications, Smart Water/Gas Meters.

(NB Smart Gas Meter Photo from Internet)
Ecosystem of Scenario, Standard and Industry Chain Driven by requirements and applications 
Infografic: IoT Ecosystem of Scenario, Standard and Industry Chain
To implement complicated scenarios with different requirements, a comprehensive industry chain including chipset and module developer, cloud platform, telecommunication operators, as well as system integrators and devices developer, would be involved.
To accelerate IoT deployment, the Solid Requirement based is critical, which is vital for IoT industry chain to work out specific total solutions and add value for all specific Things connection applications.
Big Data Values, Cybersecurity and Datasecurity Concerns
Things get connected to the Internet, and tons of Data will be generated and collected on Cloud. Data will become major energy resources, after processing by Big Data Cloud Computing, hence Data would be more valuable, requiring further innovations.
The algorithm and talent will become critical competence on application development while Cybersecurity and Datasecurity will be even more essential.

Belunn Se, senior industry observer based in Shenzhen, Guangdong province, China
(The opinions expressed here do not necessarily reflect the opinions of Panview or CCTV.com)

Panview offers a new window of understanding the world as well as China through the views, opinions, and analysis of experts. We also welcome outside submissions, so feel free to send in your own editorials to "globalopinion@vip.cntv.cn" for consideration.